
Three years ago, his age was ( x - 3) years.įive years hence, his age will be ( x + 5) years. Let the present age of Rehman be x years. (ii) 1 / x+4 - 1 / x-7 = 11 /30, x = -4, 7Ĥ. The sum of the reciprocals of Rehman's ages, (in years) 3 years ago and 5 years from now is 1 /3. Find the roots of the following equations: ∴There is no real solution of this equation.ģ. The square of a number can never be negative. On comparing this equation with ax 2 + bx + c = 0, we get On comparing this equation with ax 2 + bx + c = 0, we get Find the roots of the quadratic equations given in Q.1 above by applying the quadratic formula. Therefore, there is no real root for the given equation.Ģ. However, the square of number cannot be negative. On adding (1 /4) 2 to both sides of the equation, we get On dividing both sides of the equation, we get On adding (7 /4) 2 to both sides of equation, we get On dividing both sides of the equation by 2, we get It is given that the total production is Rs 90.∴ x(2 x + 3) = 0 Therefore, cost of production of each article = Rs (2 x + 3) Let the number of articles produced be x. If the total cost of production on that day was Rs 90, find the number of articles produced and the cost of each article. It was observed on a particular day that the cost of production of each article (in rupees) was 3 more than twice the number of articles produced on that day. A cottage industry produces a certain number of pottery articles in a day. Therefore, the base of the given triangle is 12 cm and the altitude of this triangle will be (12 - 7) cm = 5 cm.Ħ. Since sides are positive, x can only be 12. Let the base of the right triangle be x cm. If the hypotenuse is 13 cm, find the other two sides. The altitude of a right triangle is 7 cm less than its base. Therefore, two consecutive positive integers will be 13 and 14.ĥ. Since the integers are positive, x can only be 13. Let the consecutive positive integers be x and x + 1.
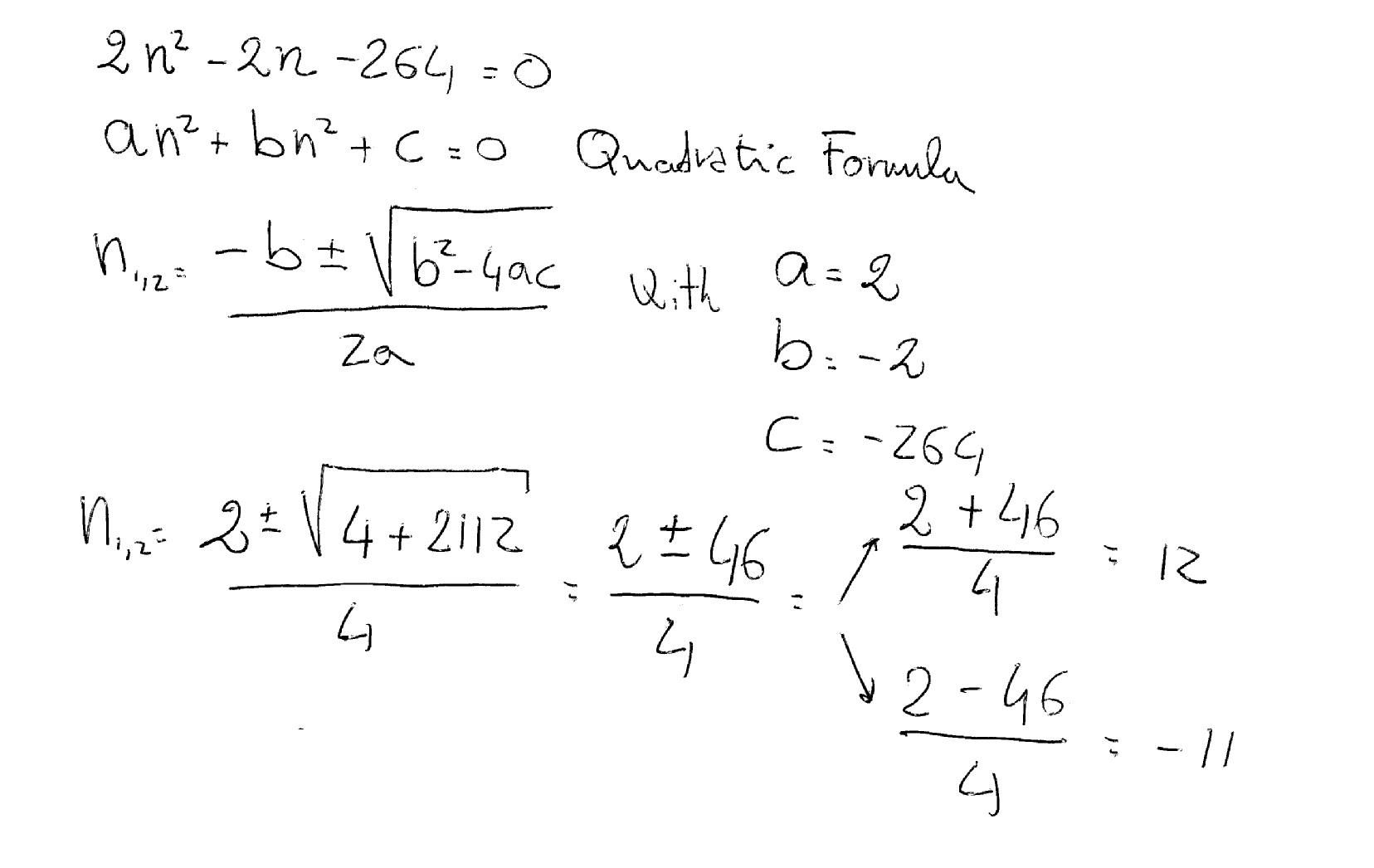
Find two consecutive positive integers, sum of whose squares is 365. It is given that the product of these numbers is 182.Ĥ. Let the first number be x and the second number is 27 - x. Find two numbers whose sum is 27 and product is 182. Hence, the number of toys will be either 25 or 30.ģ. Therefore, time taken to travel 480 km = (480 / x + 3) km/h It is also given that the train will take 3 hours to cover the same distance. In second condition, let the speed of train = ( x - 8) km/h Time taken to travel 480 km = 480 / x km/h If the speed had been 8 km/h less, then it would have taken 3 hours more to cover the same distance. (iv) A train travels a distance of 480 km at a uniform speed. The product of their ages 3 years from now will be 360 so that We would like to find Rohan's present age.Īge of Rohan's mother will = x + 26 + 3 = x + 29 The product of their ages (in years) 3 years from now will be 360. (iii) Rohan's mother is 26 years older than him. Product of both integers = x × ( x +1) = 306 Next consecutive positive integer will = x + 1 (ii) The product of two consecutive positive integers is 306. Represent the following situations in the form of quadratic equations. Hence, the given equation is not a quadratic equation.

Hence, the given equation is quadratic equation. Check whether the following are quadratic equations: This last equation is the Quadratic Formula.1. It may be helpful to look at one of the examples at the end of the last section where we solved an equation of the form as you read through the algebraic steps below, so you see them with numbers as well as ‘in general.’ Now, we will go through the steps of completing the square in general to solve a quadratic equation for x.
#Quadratic equation solution how to
We have already seen how to solve a formula for a specific variable ‘in general’ so that we would do the algebraic steps only once and then use the new formula to find the value of the specific variable. By the end of the exercise set, you may have been wondering ‘isn’t there an easier way to do this?’ The answer is ‘yes.’ In this section, we will derive and use a formula to find the solution of a quadratic equation. When we solved quadratic equations in the last section by completing the square, we took the same steps every time.

If you missed this problem, review (Figure). Before you get started, take this readiness quiz.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
